SCARS PLASTIC SURGERY
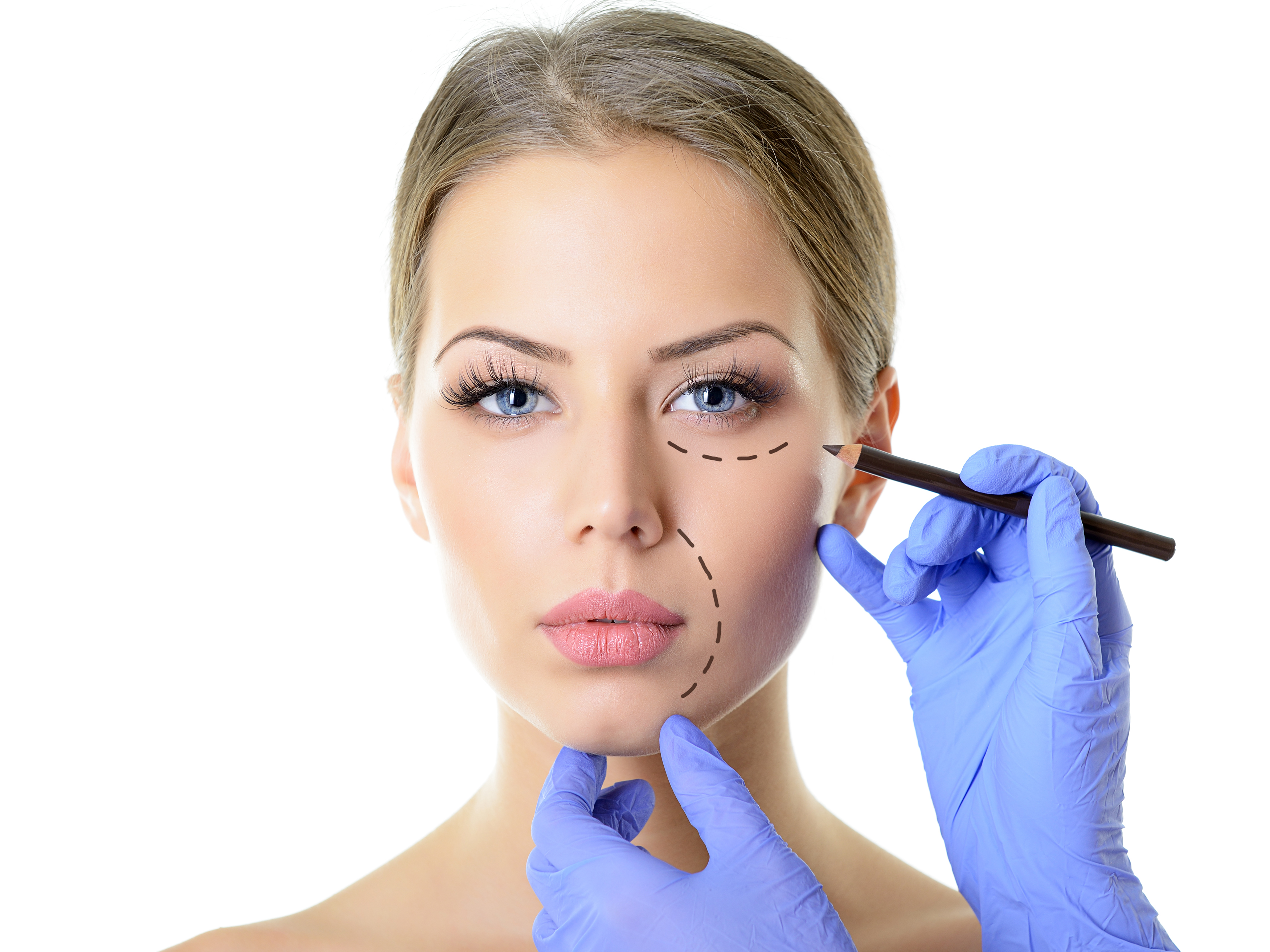
What is a scar?
A scar is the natural result of heeling the bodily injuries, which is formed due physiological process of restoring the skin or other organs.
Scar tissue differs from the surrounding tissues in its appearance, since it is less exposed to UF-irradiation and neither bears hair nor contains sudoriferous and sebaceous glands.
How does a scar look?
Most scars are pale and flat, but if our organism produces more collagen when an injury is heeled, scars may protrude over the skin surface (+ tissue) or may be located beneath the skin surface (- tissue).
Scar color may be different: from pink to purple-bluish, from white or silvery to dark-brown.
What does a scar appearance depend on?
There are many factors affecting a scar appearance:
- damage localization
- damage area
- damage depth
- damage mechanism (accident injury, surgical intervention, burn)
- heeling duration
- patient age
- heredity
- sex and race
What types of scars do exist?
- Keloid scars are of a purple-bluish color, protruding over the skin surface and often larger in area than an injury zone.
- Hypertrophic scars sometimes look like keloid ones, but rarely leave an injury boundaries.
- Atrophic scars are located beneath the surrounding skin surface (- tissue), are flat and uniformly depressed or have separate retractions. Belonging to this type may also be the so-called “extensions” formed when the skin is extended (during pregnancy or due to rapid weight changes) as well as resulting from some diseases or drug uptake.
- Contracting (vicious) scars are formed more frequent after burns. Depending on a damage depth, the muscles, tendons and nerves may be involved. The scars may limit movements.
- Postacne scars (after acne) are a direct consequence of acne disease. They may be of different types: deep, wide, narrow, flat, small and large.
Most difficult to treat are deep and narrow scars.
It should be noted that scars are impossible to be cured completely! Treatment may result in improving scar appearance only. Methods of improving scar appearance:
- Local treatment: use of external preparations applied to the scar surface, e.g. vitamin-containing, steroid-containing agents as well as a numerous group of “occlusive” preparations containing vegetable extracts and special silicon gels (gels, films). This method requires a lengthy permanent use of preparations and has excellently proven to be as a method of preventing the formation of non-esthetic scars and part of a comprehensive method supplementing the surgical treatment techniques.
- Surgical scar correction method - This method is also unable to eliminate scars completely, but enables a less visible cosmetic scar to be remained in place of a non-esthetic scar.
- Dermabrasia - This is a technique of the layer-by-layer mechanical scar removal, commonly used prior to the advent of laser resurfacing.
- Laser scar treatment - A huge laser arsenal makes it possible to improve the appearance of any scars, reduce their height and width, and improve the environment color and state.
- Injections of steroids - This is a method of injecting steroid preparations into the scar tissue, enabling hypertrophic and keloid scars to be less pronounced..
- Injections of fillers - This is a method of injecting preparations based on collagen, hyaluronic acid or fat to fill the skin (- tissue) in cases, where a scar is beneath the surrounding tissue. The result of this procedure is always temporary, and should be supported by regular secondary injections.
The most felt result is achieved is a combination of given techniques is used.
Taking into account the fact that there is no method of a complete scar removal, we recommend patients to consult a doctor immediately after trauma or surgical intervention as to the prophylaxis of a non-esthetic scar formation. In case of acne, however, the only method of scar prophylaxis is taking treatment from a dermatologist.
Med Cosmo specialists will make up a personal program of scar treatment using methods necessary for each individual case and conduct proper treatment to achieve maximally possible improvements.